How To Install Docker On Linux Rhel 7
In this 4-article series, nosotros will discuss Docker, which is an open up-source lightweight virtualization tool that runs at top of Operating Organisation level, allowing users to create, run and deploy applications, encapsulated into pocket-sized containers.
This blazon of Linux containers are proven to be fast, portable, and secure. The processes that run in a Docker container are always isolated from the principal host, preventing outside tampering.
Part 1: Install Docker and Learn Basic Container Manipulation in CentOS and RHEL 8/7
This tutorial provides a starting point on how to install Docker, create and run Docker containers on CentOS/RHEL 8/7, merely barely scratches the surface of Docker.
Stride i: Install and Configure Docker
1. Earlier versions of Docker were called docker or docker-engine, if you take these installed, you must uninstall them before installing a newer docker-ce version.
# yum remove docker \ docker-client \ docker-client-latest \ docker-common \ docker-latest \ docker-latest-logrotate \ docker-logrotate \ docker-engine
two. To install the latest version of the Docker Engine you need to set upwards the Docker repository and install the yum-utils package to enable Docker stable repository on the organisation.
# yum install -y yum-utils # yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
three. Now install the newer docker-ce version from the Docker repository and containerd manually, because due to some issues, Ruby-red Hat blocked the installation of containerd.io > i.ii.0-3.el7, which is a dependency of docker-ce.
# yum install https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/vii/x86_64/stable/Packages/containerd.io-1.ii.six-iii.iii.el7.x86_64.rpm # yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli
4. After, Docker package has been installed, start the daemon, cheque its status and enable it system-broad using the below commands:
# systemctl beginning docker # systemctl status docker # systemctl enable docker
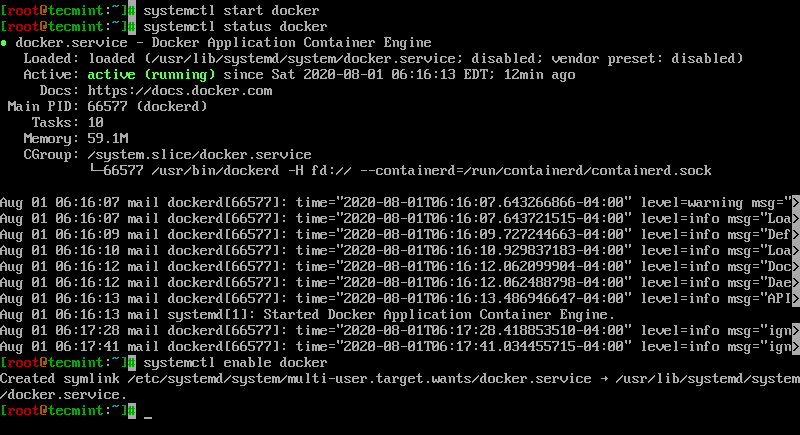
five. Finally, run a container test paradigm to verify if Docker works properly, by issuing the post-obit command:
# docker run howdy-world
If you can meet the below bulletin, then everything is in the right place.
Sample Output
Verify Docker Installation
Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker customer contacted the Docker daemon. ii. The Docker daemon pulled the "hullo-world" image from the Docker Hub. (amd64) 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that prototype which runs the executable that produces the output you lot are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminal. To attempt something more ambitious, y'all can run an Ubuntu container with: $ docker run -it ubuntu bash Share images, automate workflows, and more with a complimentary Docker ID: https://hub.docker.com/ For more than examples and ideas, visit: https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
6. Now, yous can run a few basic Docker commands to get some info about Docker:
For system-wide information on Docker
# docker info
For Docker version
# docker version
seven. To become a listing of all available Docker commands type docker on your console.
# docker
Step ii: Download a Docker Image
8. In order to showtime and run a Docker container, first, an paradigm must be downloaded from Docker Hub on your host. Docker Hub offers a lot of free images from its repositories.
To search for a Docker image, Ubuntu, for instance, consequence the following control:
# docker search ubuntu
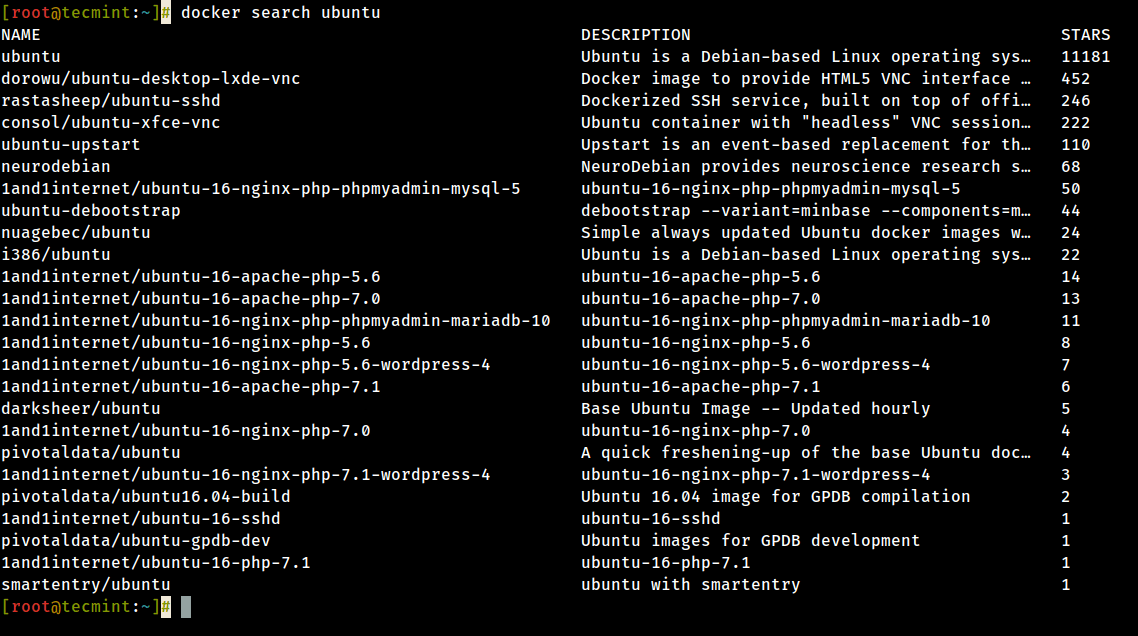
9. After you decided on what image yous desire to run based on your needs, download it locally by running the below command (in this case an Ubuntu prototype is downloaded and used):
# docker pull ubuntu
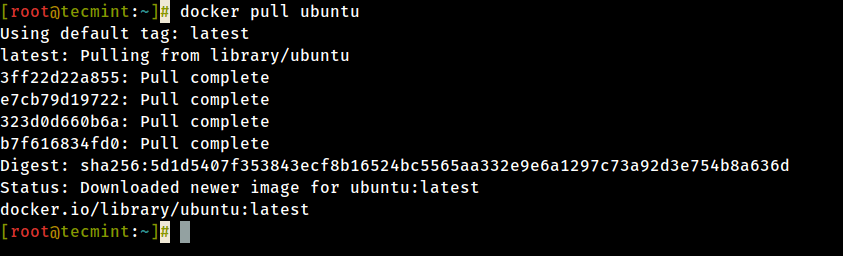
10. To list all the available Docker images on your host outcome the following command:
# docker images
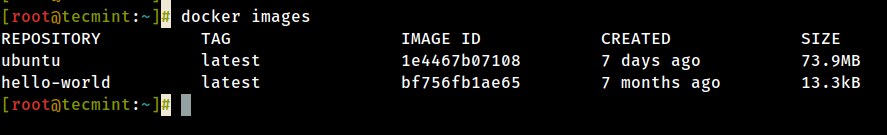
11. If yous don't demand a Docker prototype anymore and y'all want to remove information technology from the host issue the following command:
# docker rmi ubuntu
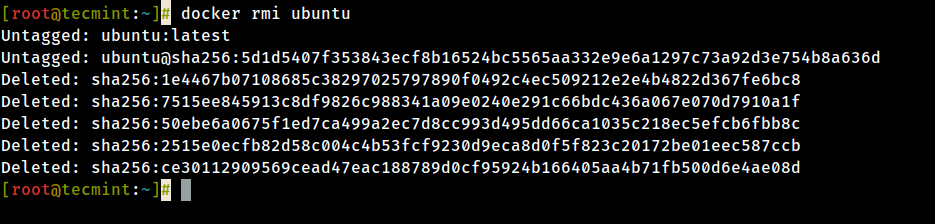
Stride 3: Run a Docker Container
When you execute a command against an image you basically obtain a container. After the control that is executing into the container ends, the container stops (you lot get a non-running or exited container). If you run some other control into the same image again a new container is created and then on.
All the containers created will remain on the host filesystem until you choose to delete them by using the docker rm control.
12. In society to create and run a container, y'all need to run command into a downloaded image, in this case, Ubuntu, so a basic control would be to display the distribution version file inside the container using cat control, as in the following example:
# docker run ubuntu true cat /etc/event
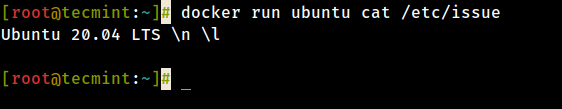
The above command is divided every bit follows:
# docker run [local image] [command to run into container]
13. To run one of the containers again with the control that was executed to create it, commencement, you must become the container ID (or the name automatically generated by Docker) by issuing the below command, which displays a listing of the running and stopped (not-running) containers:
# docker ps -l
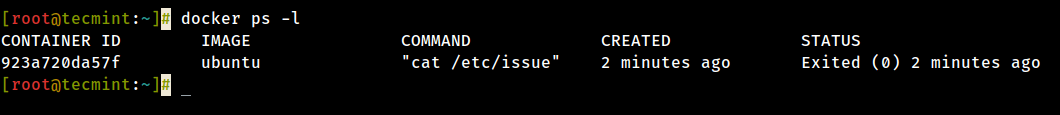
14. Once the container ID has been obtained, you can commencement the container again with the control that was used to create it, by issuing the following command:
# docker start 923a720da57f
Hither, the string 923a720da57f represents the container ID.

15. In case the container is running state, you lot can go its ID past issuing docker ps command. To end the running container upshot docker end command by specifying the container ID or automobile-generated proper noun.
# docker stop 923a720da57f OR # docker finish cool_lalande # docker ps
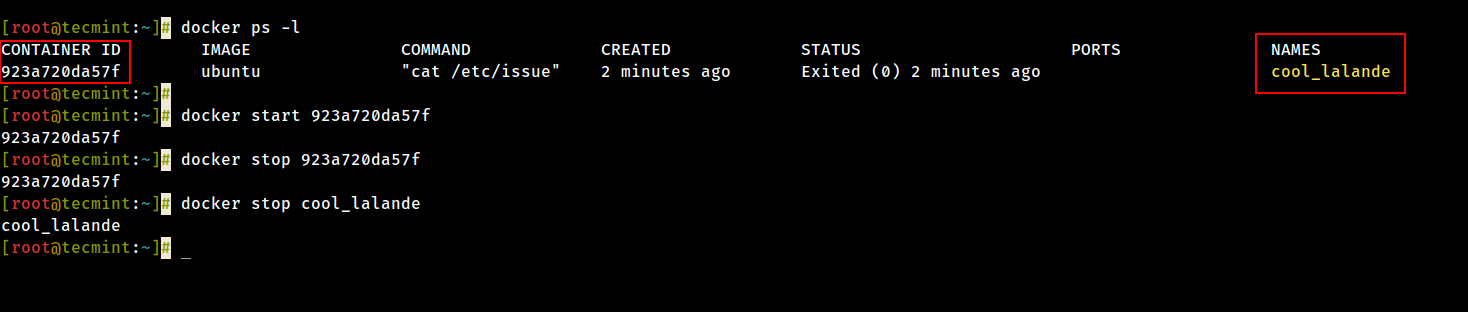
16. A more elegant culling so you don't accept to call back the container ID would be to classify a unique proper name for every container you create by using the --proper name option on the command line, as in the following case:
# docker run --name ubuntu20.04 ubuntu cat /etc/result
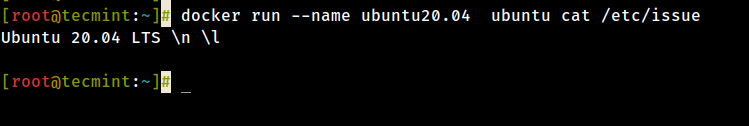
17. Then, using the name that you allocated for the container, you can manipulate container (start, stop, remove, top, stats) further just by addressing its name, every bit in the below examples:
# docker start ubuntu20.04 # docker stats ubuntu20.04 # docker top ubuntu20.04
Exist enlightened that some of the in a higher place commands might display no output if the process of command that was used to create the container finishes. When the process that runs within the container finishes, the container stops.
Footstep 4: Run an Interactive Session into a Container
18. In order to interactively connect into a container shell session, and run commands equally you exercise on any other Linux session, outcome the post-obit command:
# docker run -information technology ubuntu bash

The above control is divided every bit follows:
-
-iis used to starting time an interactive session. -
-tallocates a TTY and attaches stdin and stdout. -
ubuntuis the image that we used to create the container. -
bash(or /bin/fustigate) is the command that nosotros are running inside the Ubuntu container.
19. To quit and return to host from the running container session you must type go out command. The exit command terminates all the container processes and stops it.
# exit
20. If you're interactively logged on container concluding prompt and you demand to go along the container in running state but leave from the interactive session, you tin can quit the console and return to host last past pressing Ctrl+p and Ctrl+q keys.
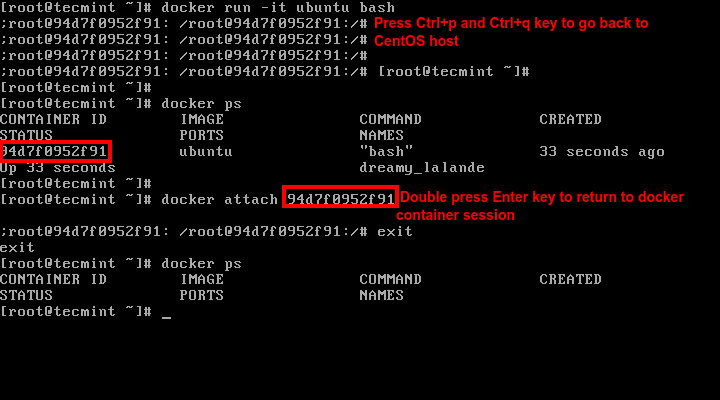
21. To reconnect to the running container you demand the container ID or proper noun. Event docker ps command to get the ID or name and, so, run docker adhere command by specifying container ID or proper name, every bit illustrated in the image above:
# docker attach <container id>
22. To stop a running container from the host session issue the following command:
# docker impale <container id>
That's all for basic container manipulation. In the next tutorial, we volition discuss how to save, delete, and run a web server into a Docker container.
Source: https://www.tecmint.com/install-docker-and-learn-containers-in-centos-rhel-7-6/
Posted by: anguloyoulderven.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Install Docker On Linux Rhel 7"
Post a Comment